


Arnavutköy is at the intersection of the subtropical high pressure belt and the low pressure belt of the cold-warm region, or the terrestrial (moisture-free) trade winds and the marine (humid and rainy) west winds. Different climatic conditions occur in winter and summer seasons with the motion of the earth.
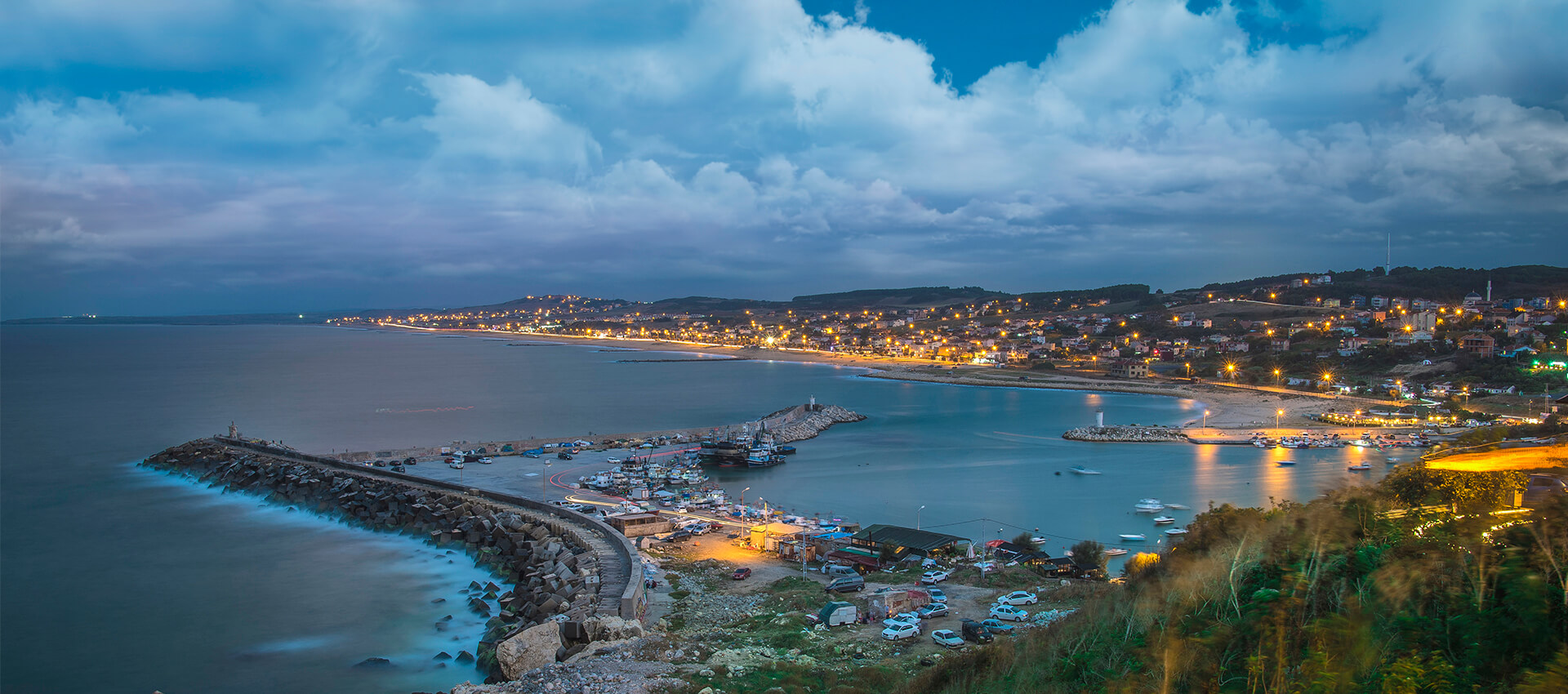
Since Arnavutköy District is located on the Black Sea coast, it features the Black Sea climate and the Mediterranean climate through the Marmara Sea. There is no possibility to evaluate the climate type in the area where Arnavutköy is located with a specific climate type only. By the nature of its geographical location and physical geography characteristics, it has different climatic characteristics than the climate of many settlements located at the same latitude.
There are three major weather types in Arnavutköy. These are calm weather types introduced from the north and south. Among the three types of weather, the one that shows the highest frequency (the highest number of blows) is the type of weather that is observed when the northern winds prevail. Arnavutköy District is located in a temperate climate zone with warm and rainy winters and hot summers. Considering that the topography and the water resources near it directly affect the climatic conditions in Arnavutköy District, it can be said that a transitional climate prevails here.
The temperature decreases in Arnavutköy when moving inland towards the Black Sea coast. The average annual temperature of the district is 14.2°C. The warmest months in the district are June, July and August, while the coldest months are January and February. The highest temperature is in July with an average of 23.8°C. The month with the lowest average temperature is February with 5.6°C (See: Table 1).
Table 1: Average Monthly Temperatures of Arnavutköy District (°C)
|
Meteorological Station
|
Months |
Annual
|
|||||||||||
| Jan. | Feb. | March. | April. | May. | June. | July. | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||
|
Florya |
5,9 | 5,6 | 7,4 | 11,8 | 16,4 | 21,2 | 23,8 | 23,6 | 20,1 | 15,8 | 11,2 | 7,8 | 14,2 |
The average rainfall of Arnavutköy District is 648.4 mm. This level is lower than the average rainfall of the coastal areas (about 1,000 mm), however it is more than the average in Turkey (about 220 mm). It can reach 864 mm around Karaburun and Yeniköy in the coastal parts of Arnavutkoy District facing the Black Sea. The highest precipitation is in November, December and January. The lowest precipitation, on the other hand, is in July and August (See: Table 2).
Table 2: Average Monthly Precipitation Values of Arnavutköy District (mm)
|
Meteorological Station
|
Months |
Annual
|
|||||||||||
| Jan. | Feb. | March | April | May. | June | July | Aug. | Sept. | Oct. | Nov. | Dec. | ||
|
Florya |
82,2 | 63,2 | 54,8 | 50,7 | 28,9 | 30,9 | 24,9 | 25,2 | 31,2 | 70.5 | 84,3 | 101,6 | 648,5 |
Although wind is an important meteorological parameter, it is very difficult to analyze this parameter since its characteristics show significant changes depending on time, location and altitude. The average annual wind speed in Arnavutköy is generally high on the Black Sea coast. The prevailing wind is the northeast wind blowing from the northeast direction.
As a result of the joint work by Istanbul Technical University (ITU) and Istanbul Water and Sewerage Administration (ISKI), the Storage Reservoir of Karaburun, Durusu-Terkos, Tahlisiye Area is fit to generate electrical energy from wind power.
The landforms determine the character of the vegetation in Arnavutköy, where all the features of the transition climate between the Black Sea and the Mediterranean climate types. Some natural reasons such as the increase in the amount of precipitation towards the northern part of Arnavutköy and the slight change in soil formation conditions have led the forests spreading in these areas to acquire the character of moist forests. Tree species in humid forests include beech, common oak, sessile oak, Istranca oak, field maple, hornbeam, chestnut and linden tree.
According to the 1/100.00-scale Istanbul Environmental Layout Plan, 57% of the district's territory (259.4 km²) appears as a forested area, however about half of it consists of well-protected areas today. The remaining part is mainly maquis shrubland, degraded forest lands or areas that have lost their forest quality. Such areas, on the other hand, are either used for agricultural purposes or are occupied by settlers.
The Terkos dunes are the largest and most important dune system found in Arnavutköy with international importance since they contain many species that are endemic to the region. There are endangered species in these dunes under the Berne Convention. According to the Berne Convention, a route change was made during the construction of the Arnavutköy-Şamlar highway to protect the plant Centaurea Hermannii (Çatalca Cornflower), a rare and endemic plant that is pledged to be protected where it is located.
Arnavutköy-Şamlar Reforestation is an important Wildlife Protection Area. There are ducks and wild geese in Lake Terkos, and wild boars, foxes, jackals, woodcock, pheasants and wild pigeons in forests. There are also buffaloes that have been separated from their herds and have become wild over time.
Forests are concentrated in the south-east, north and north-west of the district. Although records show over half of the district's territory (52%: 259.4 km²) as forest areas, only about half of it consists of well-protected areas today. The remaining part is mainly maquis shrubland, degraded forest lands or areas that have lost their forest quality. Such areas, on the other hand, are either used for agricultural purposes or are occupied by settlers.
The agricultural areas in the district consist of two parts as "absolute" and "marginal" agricultural areas. More than a third (35%: 176.4 km²) of the district's territory is agricultural land. These areas are concentrated in the south, west and central parts of the district. These regions have the form of slightly undulating plains. In addition, there are agricultural land plots among the forested areas.
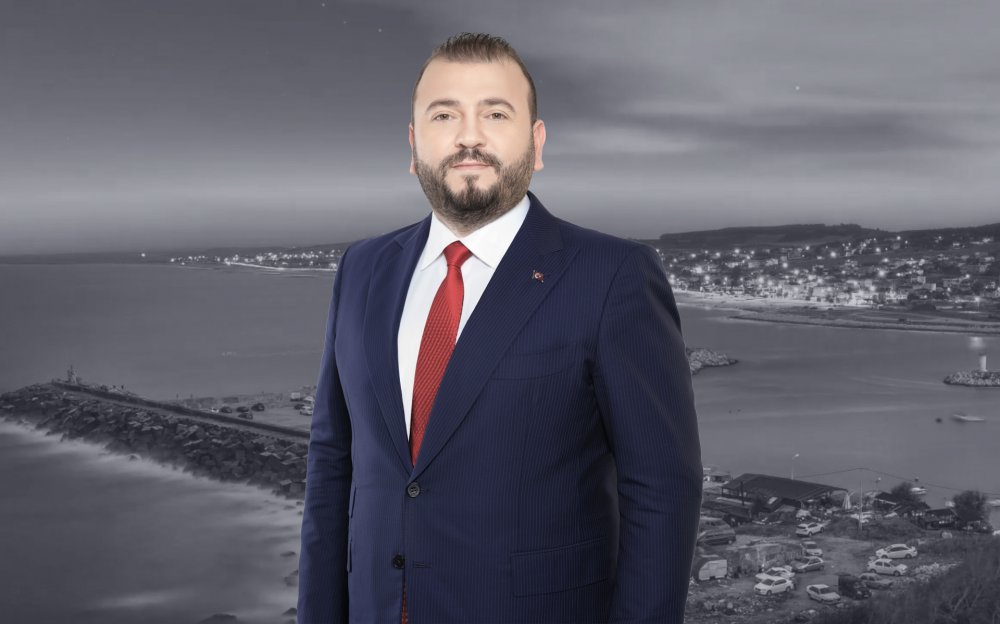






Mustafa CANDAROĞLU, originally from Cide, Kastamonu, was born on December 5, 1984, in Arnavutköy, Istanbul.
He graduated from Boğazköy Primary School in 1996, Asfa Middle School in 1999, and Sultan Fatih Anatolian High School in 2002. Completing his undergraduate education at the Faculty of Fine Arts of the International Cyprus University, Candaroğlu graduated in Interior Architecture in 2008. He completed his military service as a Short-Term Soldier at the Kayseri Regional Gendarmerie Command. After military service, Candaroğlu completed his master's education in Educational Institutions Management at Ibn Haldun University, and volunteered in various NGOs.
He served as Deputy President of the Arnavutköy Kastamonulular Association, and was a member of the boards of Arnavutköy Sports Club and Arnavutköy Beşiktaşlılar Association.
Being involved in politics throughout his education and social life, Candaroğlu served on the UNIAK Board of Directors in 2004 and actively entered politics in the Arnavutköy Belde Youth Branch in 2008. In Arnavutköy, which became a district in 2009, he held positions in District Congresses as follows: • 2009 as an Alternate Board Member of the District Primary Committee, • 2011 as a Board Member of the District Primary Committee, • 2013 as a Board Member of the District Primary Committee responsible for R&D and Local Governments. • Elected as District President in the 2018 and 2020 Congresses, Candaroğlu continues to serve as the AK Party Arnavutköy District President.
Born, raised, and currently living in Arnavutköy, Candaroğlu always finds happiness in serving in the AK Party, which practices politics based on the principle of "We love the created for the sake of the creator." After working for a long time as an Interior Architect in a family company, he continues to serve as the Chairman of the Board of Directors of Arnavutköy Bilgi Kalem College, which he founded in 2019.
Mustafa CANDAROĞLU, married and father of 3 children, speaks English proficiently.
Content is updating